Title: Immersive Realism: Unlocking the World of Full Body Photogrammetry
Introduction:
In recent years, technological advancements have revolutionised the field of 3D scanning and modelling. One particularly captivating application is full body photogrammetry, a technique that enables the creation of highly detailed and lifelike 3D models of the human body. From entertainment and virtual reality to medical applications and fashion, full body photogrammetry has opened up a world of possibilities. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of full body photogrammetry, its applications, and its impact on various industries.
Understanding Full Body Photogrammetry:
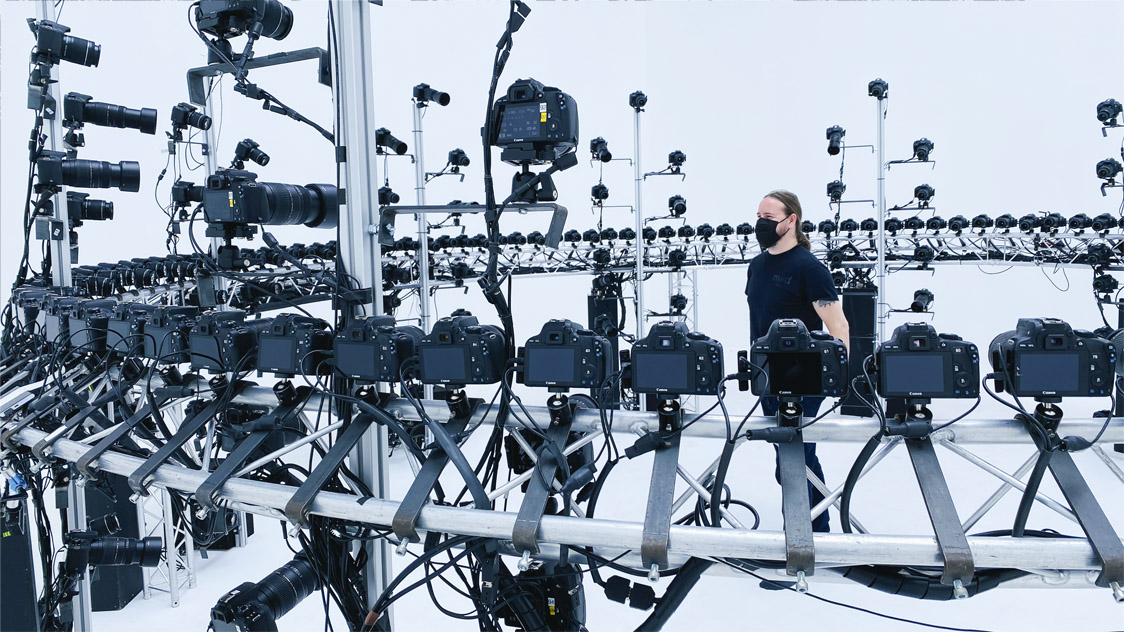
Full body photogrammetry is a process that involves capturing multiple photographs of an individual from various angles and then using specialised software to reconstruct a 3D model. The technique relies on computer vision algorithms to analyse the images and calculate the position and shape of the subject’s body in three-dimensional space.
The Process:
The process of full body photogrammetry typically involves the following steps:
1. Image Capture: The subject stands on a platform or a designated area while a series of high-resolution photographs are taken from multiple angles. The more photographs captured, the more accurate and detailed the resulting 3D model will be.
2. Image Processing: The collected images are then fed into photogrammetry software that utilises sophisticated algorithms to identify common points and create a point cloud. This point cloud represents the 3D positions of the subject’s body in the images.
3. Mesh Creation: The point cloud is used to generate a mesh, which is a connected network of polygons that defines the surface of the 3D model. The software uses the point cloud as a reference to determine the shape and contours of the subject’s body accurately.
4. Texture Mapping: Once the mesh is created, the software projects the original images onto the surface of the model, giving it realistic texture and color information. This process adds depth and enhances the visual realism of the final 3D model.
Applications of Full Body Photogrammetry:
1. Entertainment and Gaming: Full body photogrammetry has significantly impacted the entertainment industry, particularly in the realm of video games and virtual reality experiences. By capturing the likeness of real-life actors or individuals, game developers can create incredibly realistic character models that enhance immersion and storytelling.
2. Fashion and Retail: The fashion industry has also embraced full body photogrammetry as a tool for virtual try-on experiences. With accurate 3D models of customer bodies, it becomes possible to visualise how different clothing items fit and look without physically trying them on, revolutionising the online shopping experience.
3. Medicine and Rehabilitation: In the medical field, full body photogrammetry plays a crucial role in areas such as orthotics, prosthetics, and rehabilitation. By scanning patients and generating precise 3D models, healthcare professionals can design custom-fit braces, prosthetic limbs, and assistive devices, ensuring a better fit and improved patient outcomes.
4. Anthropology and Forensics: Full body photogrammetry finds applications in anthropology and forensics as well. It allows researchers to digitally preserve and study ancient artefacts, fossils, and human remains. In forensic investigations, this technology aids in crime scene reconstruction, facial reconstruction, and body identification.
The Future of Full Body Photogrammetry:
As technology continues to advance, full body photogrammetry is expected to become even more accessible and refined. With the rise of consumer-grade depth-sensing cameras and the integration of AI algorithms, capturing high-quality 3D models may become as simple as taking a regular photograph.
Moreover, advancements in real-time rendering and virtual reality technologies will enable interactive experiences where users can explore and interact with photorealistic 3D models of themselves and others.
Conclusion:
Full body photogrammetry has emerged